- Home
- Publications
- A Comparison Of Earnings Related To Higher Level Vocational/Technical And Academic Education
A Comparison of Earnings Related to Higher Level Vocational/Technical and Academic Education
 Pub. Date
Pub. Date
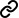 Pub. Type
Pub. Type
Downloads
DP502: A Comparison of Earnings Related to Higher Level Vocational/Technical and Academic EducationRelated Themes
Education and SkillsJEL Code
I21, I24, I26, J64
Paper Category Number
502
We use the earliest cohort of English secondary school leavers with newly available Longitudinal Education Outcomes data (622,000 pupils in 2002/03) to compare earnings of people with higher vocational/technical qualifications to those of degree holders. The unusually rich data allow us to estimate earnings differentials until the age of 30, controlling for a wide array of characteristics and full education trajectories.
Our results show that initially higher earnings observed for people achieving higher vocational education disappear when people are in the mid-twenties. Depending on the type of university attended, male degree holders earn up to 18% more by age 30, while female graduates earn around 40% more. However, there is considerable heterogeneity by gender and subject area. There are high returns related to higher vocational/technical education in STEM subjects, which remain significantly above those of many degree holders by age 30.
Related Blog Posts

What Can Be Done To Better Protect Children and Young People From Serious Safeguarding Incidents?
Sophie Kitson
Ekaterina Aleynikova
19 Feb 2024
9 min read

Putting Increased Pressure on a Fragile System Does Not Help
Claudine Bowyer-Crane
Cecilia Zuniga-Montanez
15 Jan 2024
5 min read


Safeguarding the Safeguards – more Support Needed, But How?
Lucy Stokes
Johnny Runge
Adrian Pabst
02 May 2023
6 min read
Related Projects

Catch Up Literacy Pilot Study

Better Start Bradford
Related News


Press Release: Targeted home support could be key in children’s early language development
21 Apr 2021
5 min read
Related Publications


The Nature of the Inflationary Surprise in Europe and the USA
21 Mar 2024
Discussion Papers

Energy and Climate Policy in a DSGE Model of the United Kingdom
08 Mar 2024
Discussion Papers



