- Home
- Publications
- Modelling The Economic Effects Of Trade Policies – A Submission To The Treasury And International Trade Committees Inquiry Into Implications Of The UK’s Approach To International Trade
Modelling the Economic Effects of Trade Policies – A Submission to the Treasury and International Trade Committees inquiry into implications of the UK’s approach to international trade
 Pub. Date
Pub. Date
11 July, 2018
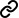 Pub. Type
Pub. Type

Abstract
- Computable General Equilibrium (CGE) trade models are helpful and widely used laboratories to study the economic effects of changes in trade policy and in particular different Brexit scenarios.
- Both the calibration of the structural parameters of the model (e.g. trade elasticity) and the quantification of future trade tariffs and non-tariff costs are of the first order importance for any counterfactual evaluation.
- Any counterfactual scenario of Brexit evaluated in a CGE framework should be assessed against credibility and limitations of its assumptions, and calibration of its crucial parameters. Extreme assumptions often lead to extreme results.
- There are many channels not included in CGE models and which are very likely to impact the UK economy after Brexit (foreign direct investment, additional productivity channels, the role of global value chains, etc.).
Related Blog Posts
Blog
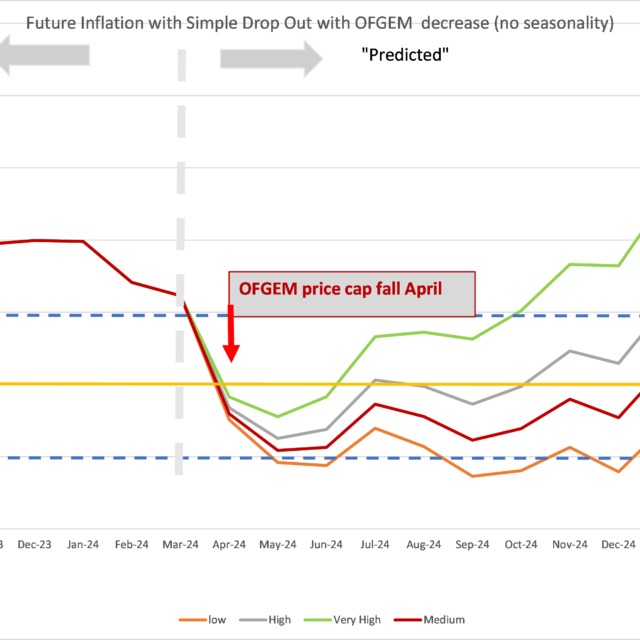
Inflation Still Likely to Fall to 2 per cent or Below Next Month
Huw Dixon
17 Apr 2024
8 min read


Blog
What is the Current State of the UK Economy?
Paula Bejarano Carbo
Stephen Millard
26 Feb 2024
7 min read
Related Projects
Related News
news
Why it’s not worth worrying that the UK has technically entered a recession
26 Feb 2024
4 min read
news
1.2 million UK Households Insolvent This Year as a Direct Result of Higher Mortgage Repayments
22 Jun 2023
2 min read

news
The Key Steps to Ensuring Normal Service is Quickly Resumed in the Economy
13 Feb 2023
4 min read
Related Publications

publication
Recessionary Pressures Receding in the Rearview Mirror as UK Economy Gains Momentum
12 Apr 2024
GDP Trackers
Related events

Summer 2023 Economic Forum
NIESR is delighted to bring to you our latest Economic Forum where we presented our forecast for the next economic quarter. With inflation remaining stubbornly high, a labour market that...
11:00 to 12:00
11 August, 2023

Spring 2023 Economic Forum
NIESR is delighted to bring to you our latest Economic Forum where we present our forecast for the next economic quarter. As King Charles III is officially crowned, and the...
11:00 to 12:00
12 May, 2023

Winter 2023 Economic Forum
With recent UK GDP figures prompting a cautious optimism amongst some analysts, the question has arisen around whether the UK can avoid a recession? Was the 0.1% growth in November...
11:00 to 12:00
10 February, 2023

Autumn 2022 Economic Forum
Join us, the day after the Chancellor’s autumn statement, to hear our analysis of the measures announced and their likely impact at both a UK, and individual household, level. Utilising...
11:30 to 12:30
18 November, 2022
Summer 2022 Economic Forum
We are delighted to invite you to our Summer 2022 Economic Forecast, where we will present and discuss NIESR’s latest forecasts on the UK and global economies, with an opportunity...
11:00 to 12:00
5 August, 2022

Spring 2022 Economic Forum
We are delighted to invite you to our Spring 2022 Economic Forecast, at which we will present and discuss NIESR’s latest forecasts on the UK and global economies, with an...
11:00 to 12:00
13 May, 2022

Winter 2022 Economic Forum
With rising inflation asking questions of central banks, consumer incomes hit by rising energy prices and Omicron continuing to disrupt the supply of both goods and labour, what does the...
11:00 to 12:00
11 February, 2022

Autumn 2021 Economic Forum
We are delighted to invite you to our Autumn 2021 Economic Forum, at which we will present and discuss NIESR’s latest forecasts on the UK and global economies, with an opportunity for you to ask questions.
11:00 to 12:00
12 November, 2021